ExoRomper
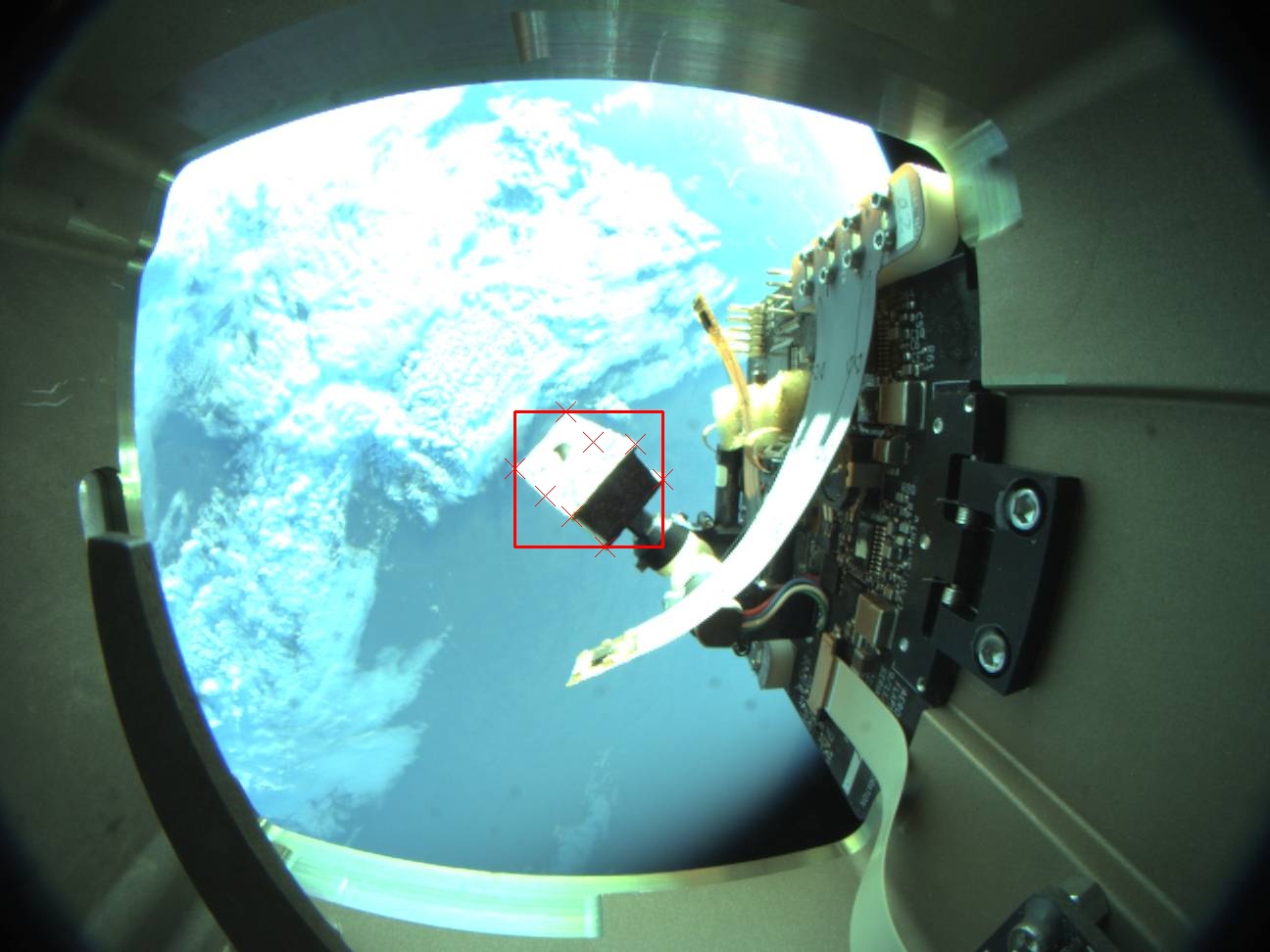

ExoRomper is a payload onboard Aerospace’s Slingshot-1 space vehicle. The payload is testing ML-based satellite pose estimation algorithms and ML Ops for space applications. With this payload, we are iteratively updating, deploying, and validating ML models that operate onboard vehicles in space, in this case for satellite pose estimation.
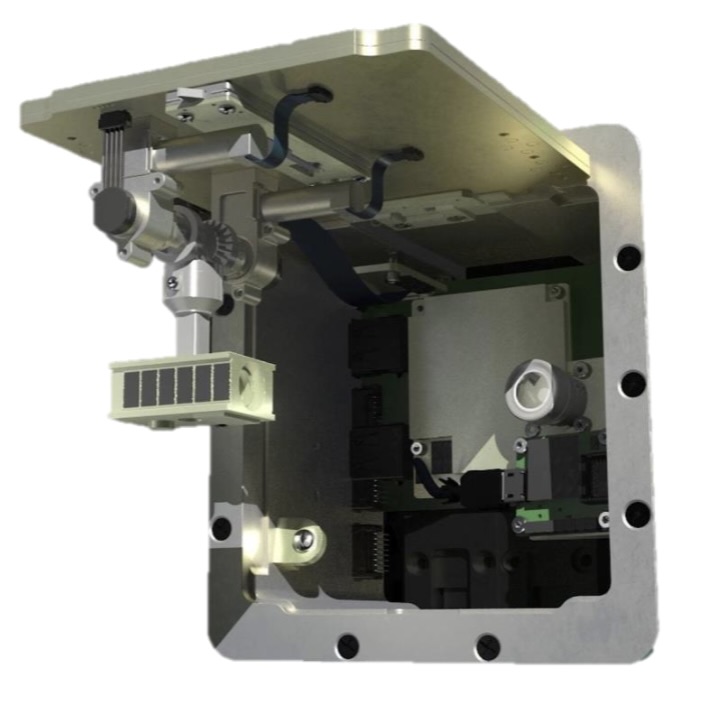
My role on the team was to:
- Implement the satellite pose estimation algorithm using CNNs implemented in TensorFlow/tflite, PnP from OpenCV, and Python, all deployed to a Google Coral SOM
- Collect and label operational data for CNN training
- Set up and run an ML Ops pipeline using Data Version Control (DVC) to train new models, track all model/code/data changes, and produce more accurate CNNs and thus a more accurate satellite pose estimation algorithm
For more on the workings of the algorithm, see the paper we wrote: Capabilities Toward Trustable AI/ML Pose Estimation for Satellite-to-Satellite Imagery.